The First Australian Multi-Centre Study of Dementia using Ultra-High Field MRI
Australia is at the forefront of dementia research with world leading studies such as the Australian Imaging and Lifestyle study of Ageing (AIBL) led by a consortium of Australia’s leading Dementia centres, and the recently started Prospective Study of Ageing (PISA) led by the QIMR Berghofer.
The installation of the first human ultra-high field MRI scanner in the southern hemisphere at the Centre for Advance Imaging, the Qld node of the National Imaging Facility, in 2014 opened up a new era of imaging research. The Siemens 7T whole-body MRI scanner brought Australia to the forefront of ultra-high field research enabling examination of the human brain with an unprecedented level of detail.
Subsequently, a second 7T scanner was installed at the Melbourne Brain Centre providing a unique opportunity for a national multi-centre collaboration in ultra-high field MRI and the capability to explore new imaging biomarkers for diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease. A major project is underway, led by the Brisbane-based CSIRO eHealth Research Centre, co-funded by the CRC for Mental Health and in collaboration with the QIMR Berghofer, University of Melbourne and Florey Institute for Neuroscience with the broad aim of characterising new bioimaging biomarkers of neurodegeneration in the aging population. A suite of MRI methods is being applied at both sites on large cohorts of healthy aging subjects and patients diagnosed with fronto-temporal dementia. The scanning part of the project has been successfully completed with superb image quality obtained using state of the art sequences. A significant effort is now underway to analyse this valuable data which may contain a wealth of diagnostic information not otherwise available.
This story was contributed by The University of Queensland
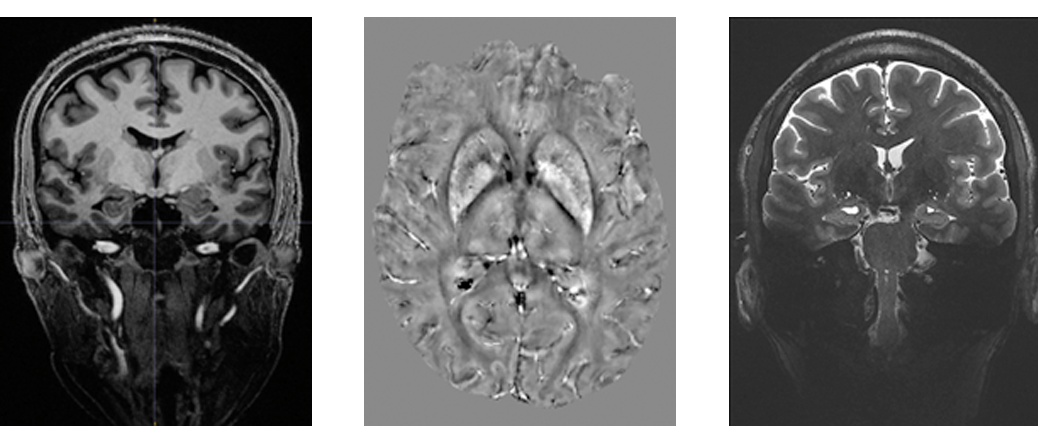
Feature image: (Left) 3D MP2RAGE 0.9mm isotropic showing exceptional tissue contrast, (centre) example of a Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM), a mechanism for useful chemical identification and quantification of specific biomarkers, and (right) T2W TSE using coronal accquisition for hippocampus subfield examination.