Grape split imaging to examine physical changes before and after splitting using diffusion magnetic resonance
Berry split is a condition in which the grape epidermis splits which often occurs during periods of high rainfall and is a significant cause of grape crop loss. In damp conditions there is increased uptake of water via osmosis and decreased water loss from transpiration. The pre-dawn turgor pressure of table grape cultivars lies in the vicinity of 5-38 kPa but prior to berry split can be as high as 1.5-3.7 MPa.
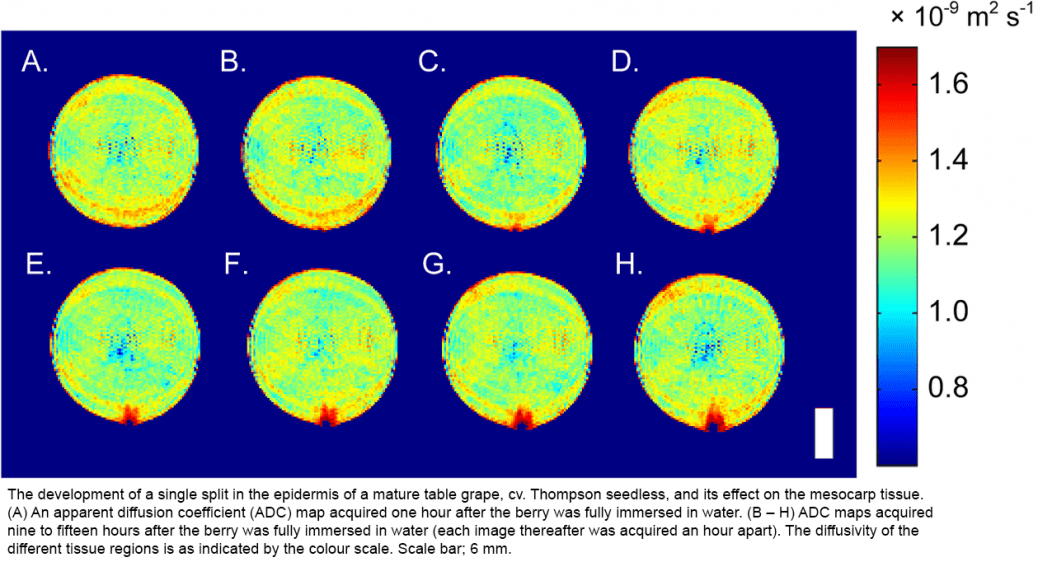
In order to examine and characterise the immediate effect of fruit split on grape, National Wine & Grape Industry and Western Sydney University node of National Imaging Facility have been collaborating on an ongoing project, which investigates the physical changes within the grape berry both before and after splitting using diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. Thirty-six table grapes of the Thompson Seedless variety were involved in the study and assigned to three groups: a control group (12 berries), a group in which they were wrapped in damp tissue (12 berries), and a total immersion group (12 berries). Five axial images (including diffusion tensor images) spaced evenly apart along the length of each berry were acquired simultaneously every hour to create a time-course study of each grape.
For each grape that split within the MRI during the study it was observed that there was an immediate change in the diffusion coefficient in the region of the wound. This region increased in volume over the course of the subsequent scans and correlated with regions of non-vital cells (as determined by fluorescence microscopy). It was determined from the study that grape berries left exposed to standing water after splitting exhibit greater cell death within the vicinity of the split. Therefore, the surface of split berries should be kept dry if possible to reduce further damage.
Collaborators
Nanoscale Organisation and Dynamics Group, University of Western Sydney
School of Medicine, University of Western Sydney
National Wine & Grape Industry Centre
NSW Department of Primary Industries
Sources
Dean, R.J., Bobek, G., Stait-Gardner, T., Clarke, S.J., Rogiers, S.Y. and Price, W.S. (2015), Time-course study of grape berry split using diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. Aust. J. Grape Wine R. doi: 10.1111/ajgw.12184
Dean R.J., Stait-Gardner, T., Clarke, S.J., Rogiers, S.Y., Bobek, G. and Price, W.S. (2014) Use of diffusion magnetic resonance imaging to correlate the developmental changes in grape berry tissue structure with water diffusion patterns. Plant methods 10(1):35